Friction welding is superior for welding stainless steel to carbon steel components compared to conventional weld processes. Our process never uses filler metals or weld deposits and requires minimum pre-weld joint preparation, displacing oils, oxidation, and other contaminations during the welding phase. The dissimilar metals reach a plasticized state before forging, creating a very narrow heat-affected zone (HAZ), protecting the molecular structure of the components while eliminating porosity and hot cracking. Friction welding creates a bond as strong as the base materials.
Friction Welding Specifications
AFW employs state-of-the-art computer-controlled rotary friction welding centers for precise and reliable results. Our weld process follows a Weld Procedure Specification (WPS) that sets specific tolerance parameters for every part. Equipped with advanced high-precision controllers, our welding centers meticulously monitor all critical variables throughout the weld cycle to guarantee product conformance – RPMs (rotations per minute), PSI (weld pressure), and total stock length loss. Controlling forge ramp and deceleration is critical in maintaining consistent and standardized welds. The operator receives immediate notification if a weld parameter is out of range to take corrective action. We record data from each weld cycle for future parameter review and analysis.
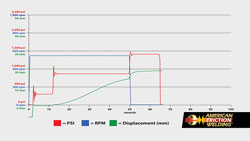
This graph displays the RPMs, PSI, and stock displacement from the abovementioned Stainless to Carbon Friction Welding video.
SS to CS FRW 100X Magnification
Shown is a 100X magnification of the stainless steel to carbon steel rotary friction weld. There is a clear definition of the base metals at the top and bottom, with the friction weld located in the center of the image. The narrow heat-affected zone (HAZ) is evident by examining the intact molecular structure of the parent metals aligning the friction weld zone.
SS to CS Weld Bend Test
Friction welding bend tests are common to assess welded joints’ mechanical integrity and bonding strength. This testing method involves subjecting a friction-welded specimen to bending forces, which simulate real-world conditions and evaluate the weld’s resistance to deformation. A predetermined load is applied gradually to the sample during the test to achieve the desired bend angle. The test measures parameters such as the ultimate bending moment, the yield strength, and the ductility of the weld. By performing friction welding bend tests, engineers and researchers gain valuable insights into the quality and reliability of friction-welded joints, helping to ensure the structural integrity and performance of welded components in various applications.
Welding stainless steel to carbon steel can be required in specific applications where combining different materials is necessary. Here are a few reasons to weld carbon to stainless steel:
- Structural Integrity: Combining carbon steel and stainless steel can provide a balance between strength and corrosion resistance. Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability, while stainless steel offers excellent resistance to corrosion. By welding these two materials together, you can achieve a strong and corrosion-resistant structure, making it suitable for various applications.
- Cost Savings: Stainless steel is generally more expensive than carbon steel. In some cases, welding dissimilar metals can be a cost-effective solution, especially when the stainless steel component is small and only needs to be joined to the carbon steel structure. You can save on material costs by using carbon steel for most of the design and only incorporating stainless steel where necessary.
- Compatibility with Different Environments: Certain applications require parts that can withstand different environments simultaneously. For example, in the chemical industry, where corrosive substances are present, a structure may need to handle both acidic and high-temperature conditions. You can use carbon steel’s high strength and stainless steel’s corrosion resistance, making it suitable for such demanding environments.
- Thermal Expansion Considerations: Carbon steel and stainless steel have different coefficients of thermal expansion, meaning they expand and contract at different rates when exposed to temperature changes. Friction welding makes joining these dissimilar materials possible while minimizing the risk of stress and distortion caused by thermal expansion differences.
- Hybrid Designs: In some cases, a product may require different properties in different areas. Welding stainless to carbon allows for hybrid designs that combine the desired properties of each material. This approach is particularly relevant in industries such as aerospace or automotive, where lightweight structures with high strength and corrosion resistance are essential.
It’s important to note that welding carbon steel to stainless steel can be challenging due to the differences in material properties and the potential for galvanic corrosion. Friction welding is a strong and durable weld joint. Consult our qualified engineers and specialist to ensure a successful welding process and to address any specific considerations for your application.
- Melting Point: 2,550 - 2,790°F | 1,400 - 1,530°C
- Thermal Conductivity: 15 W/m-K (watts per meter per kelvin)
- Grades: Austenitic Stainless Steel, Ferritic Stainless Steel, Duplex Stainless Steel, and Martensitic Stainless Steel
- Melting Point: 2,597 - 2,800°F | 1,425 - 1,540°C
- Thermal Conductivity: 45 W/m-K (watts per meter per kelvin)
- Grades: Low Carbon Steels | Mild Steel (up to 0.3% carbon), Medium Carbon Steels (0.3–0.6% carbon), and High Carbon Steels (more than 0.6% carbon)
Other Welding Combinations: Carbon Steel to Stainless Steel, Copper to Aluminum, Hastelloy Welding, Inconel to Inconel, Nitronic 50, Stainless Steel to Mild Steel, Stainless to Stainless


